Cystic lung disease
Van Holden, M.D.
Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Fellow
University of Maryland Medical Center, Baltimore, MD
Case:
A 33 year-old woman with a history of uterine fibroids and iron deficiency anemia presented with progressively worsening dyspnea on exertion for 2 years. She reported shortness of breath with climbing one flight of stairs. She had an associated dry cough and intermittent sharp right-sided chest pain.
Social History: Smokes 3-5 cigarettes per day for 15 years. Drinks alcohol occasionally. Prior history of smoking marijuana. Has had 1 sexual partner.
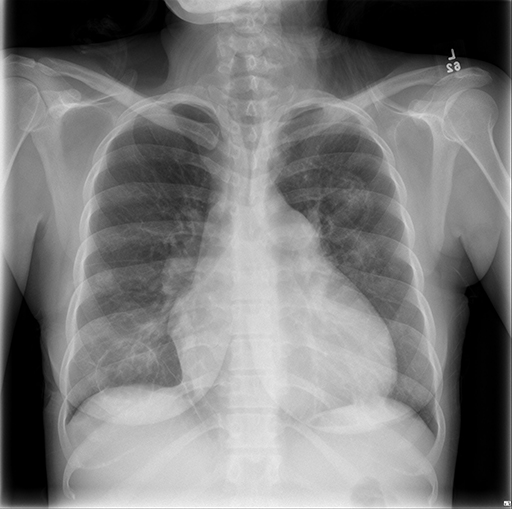
Vital signs and cardiopulmonary exam were normal. Basic labs and EKG were also normal. Due to an elevated D-dimer of 570 ng/mL, she had a CTA chest done.
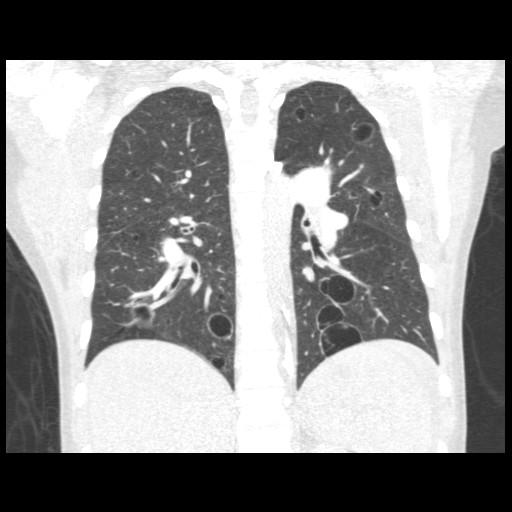
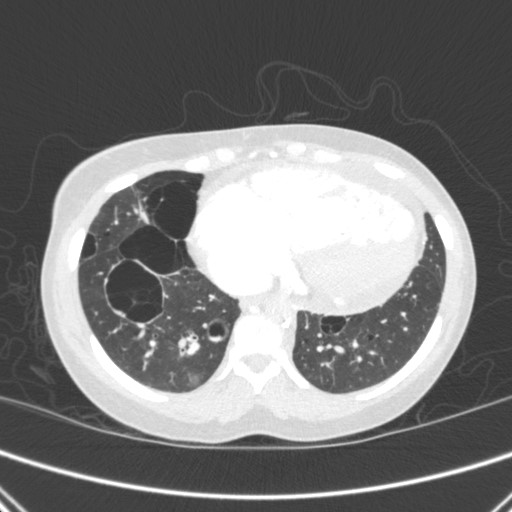
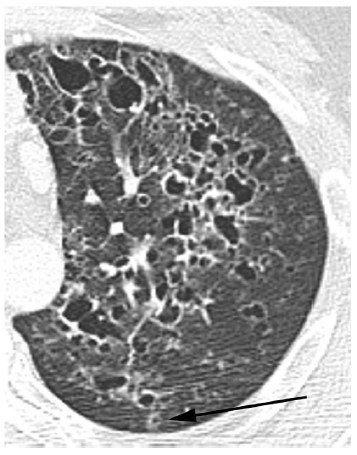
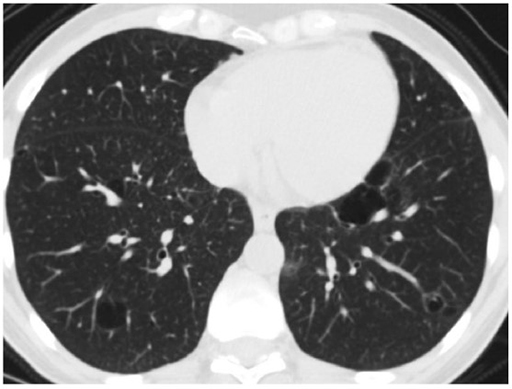
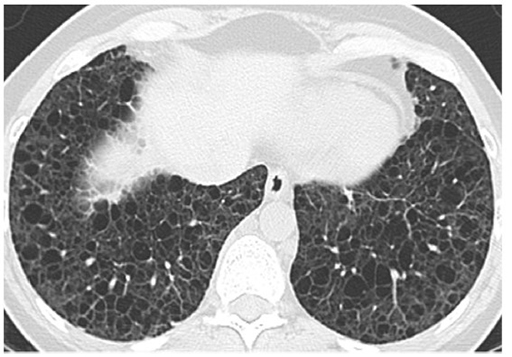
CXR and CT chest
What is the most likely etiology of her diffuse cystic lung disease?
- Pulmonary Langerhans cell histiocytosis
- Lymphoid interstitial pneumonia
- Lymphangioleiomyomatosis
- Emphysema
Correct Answer 2
Work-up revealed HIV positivity. Subsequent pathology from transbronchial biopsies was consistent with a diagnosis of lymphoid interstitial pneumonia.
The Fleischner Society defines a cyst as a "round parenchymal lucency or low-attenuating area with a well-defined interface with normal lung and a wall thickness < 2mm." A cavity, on the other hand, has a wall thickness > 2 mm. Other cyst mimics include emphysema, pneumatoceles, bronchiectasis, and honeycombing.
Differential of Cystic Lung Disease
Pulmonary Langerhans cell histiocytosis
Lymphoid interstitial pneumonia
Lymphangioleiomyomatosis
Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome
Erdheim Chester disease
Follicular bronchitis
Sarcomas
Pleuropulmonary blastoma
Light chain deposition disease
Amyloidosis
Sjogren syndrome
Pneumocystis jiroveci
Recurrent respiratory papillomatosis
Desquamative interstitial pneumonia
Post-traumatic pseudocysts
We review the 3 answer choices here.
References:
-
Gupta N, Vassallo R, Wikenheiser-Brokamp KA, et al. Diffuse cystic lung disease part I. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2015;191(12):1354-1366.
-
Gupta N, Vassallo R, Wikenheiser-Brokamp KA, et al. Diffuse cystic lung disease part II. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2015;192(1):17-29.
-
Hansell DM, Bankier AA, MacMahon H, et al. Fleischner Society: Glossary of terms for thoracic imaging. Radiology 2008;246:697-722.
-
Jawad H, Walker CM, Wu CC, et al. Cystic interstitial lung diseases: recognizing the common and uncommon entities. Curr Probl Diagn Radiol 2014;43:115-127.